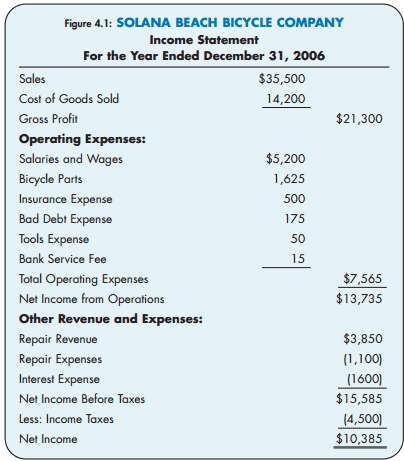
Basics of the income statement
The basic information on the income statement is not enough to create a solid financial model. A successful business must be able to calculate net income and its associated costs. Net income is calculated by deducting the liabilities from the equity and reducing the cost of revenue by the amount of revenue. This number includes interest, tax payments, and capital depreciation. It provides a complete picture of the health of the business and the potential for profit. A positive income statement means that revenues exceeded expenses. If the other way around, the result is a negative income statement.
When a company generates profits, it reports their profit over a period of time. The time period could be one week, a month, five weeks, or a year. The amount earned during each period is then divided by the total cost of revenue. Profitability is therefore shown as a positive number. Other revenues and gains include interest and dividend income, as well as gains on the sale of assets. These are not directly related to the business, but are recorded as revenue. For example, EA will report a gain when it sells a car while Audi will report a revenue from the sale of the car.
Revenues are the money that the business receives from operations. Revenues are usually reported separately from expenses. The revenue section can be broken down by geography and business unit. A company can also record gains, which represent the net proceeds from peripheral activities. Gains are listed separately from expenses in the income statement. They do not form an integral part of the company’s everyday operations. Examples of gains include the proceeds from selling investments, asset disposals, and lawsuits.
Revenue and cost of sales are key components of the income statement. They are not separate from costs, and are directly related to the generated revenue. For example, EA reports server fees as part of its cost of sales. By examining these metrics, the business can understand its profitability better. And these are only the basic components of the income statement. With the proper understanding of the income statement, you can make the right decisions based on the data available.
Operating expenses are costs that keep the business going. These costs are often reported in one section with cost of goods sold. However, most businesses use a multi-step format to break down operating expenses into multiple line items. In this way, they make the income statement look more streamlined. There are three types of operating expenses that are included in the income statement. However, not all expenses are equal. Therefore, it is important to consider how they are calculated.
Liabilities are the other essential component of the financial statements. They are categorized as either current or non-current. Current liabilities are those that settle within 12 months. Examples of current liabilities are salaries payable. Non-current liabilities are those that are expected to settle in more than twelve months. Long-term liabilities, on the other hand, are those that are expected to last for more than twelve months. The basic elements of the income statement are the balance sheet.
External users of the income statement
The income statement can be useful to an investor as they can gauge the financial health of a company. Potential investors, unions, and creditors may also be interested in the financial results of a business. Other potential users of financial information include the general public, employees, and creditors. Listed below are some of the reasons why investors need to examine the financial statement of a company. While these users have different needs and goals, the income statement provides information to all of them.
Creditors: Creditors will want to see a company’s income and expenses in order to determine whether or not the firm is able to pay its bills. They will also be interested in the current ratio of the organization. Depending on the results of the financial statement examination, a lender may decide to extend credit or not. Customers: If a company has a weak financial position, customers may take their business elsewhere.
External users: People outside of the company who rely on financial accounting information to make decisions. The purpose of financial accounting is to capture and communicate important business events for the benefit of external users. Since these people have no firsthand knowledge of a company’s financial position, they rely on the information provided by the business. This information is critical to their decisions. In addition to financial analysts, external users are used by investors and potential investors.
Financial ratios derived from the income statement
Financial ratios are important indicators of a company’s performance, and are calculated from the income statement’s revenue line items. They provide information on the ability of a company to generate profit and cover debts. Different financial statements have different formulas for calculating these ratios, and financial advisors and corporate annual reports can use Einstein-level calculations to determine a company’s health. Business owners, however, can use the most basic ratios to judge a company’s performance.
For a more detailed explanation of these ratios, read Handbook of Financial Analysis for Managers, published by the American Management Association. The Risk Management Association also publishes Annual Statement Studies, which include data for 325 business lines sorted by sales volume and asset size. They also list the common size of each balance sheet. The Almanac of Business and Industrial Financial Ratios, published by Leo Troy, contains detailed information on various financial ratios for more than 150 industries.
In addition to gross margin, the income statement also shows operating margin, profit margin, earnings per share, and operating margin. The latter two ratios help investors determine how much they should invest to earn one dollar of revenue. If a company’s gross margin is 40 percent, they’re keeping 40 cents for every dollar of revenue, and spending the rest on operating expenses. However, there are concerns about manipulation of this metric.
Financial ratio analysis is a critical component of analyzing a company’s performance. The results of financial ratio analysis can be used to evaluate a company’s liquidity, profitability, growth, and leverage. By tracking the changes in the ratios over time, it can help investors make decisions about whether to invest in the business or extend credit. Further, financial ratio analysis is an essential tool for performance management and benchmarking.
Another measure of a company’s efficiency is the investment turnover. This ratio is often high or low, depending on the industry. A high investment turnover indicates that the company has effectively deployed its assets and is producing good sales numbers. Another useful measure of productivity is the sales per employee ratio. This ratio varies from industry to industry, but a high one indicates that the company has great personnel and equipment. This ratio can help investors decide if the company’s management is performing as well as it should.
A third way to evaluate a company’s liquidity is to analyze its debt-to-equity ratio. This ratio is a simple way to measure how much of a company’s assets are secured by debt. The current ratio measures the company’s assets and liabilities and represents how liquid the business is. The higher the ratio, the more liquid the assets. Therefore, the better. A higher ratio indicates that a company can pay off its liabilities and meet its obligations.
The best way to know how much revenue your business is generating is to prepare performance reports alongside other financial reports. To prepare your income statement, you need to create a test balance sheet, calculate your income, determine cost of goods sold, calculate gross margin, include operating expenses, calculate your income including income tax, calculate net income, and finally complete your income statement , with company and reporting period data. Financial reporting can help investors and lenders determine a company’s past financial performance, predict future results, and use the income statement to assess the ability to generate future cash flows.
This article covers the Basics of the Income Statement, External users and Financial ratios derived from the statement. If you are unsure about the basics of the income statement, read on! There are many things you need to know about this document. Read on to discover the basics of the income statement and how to interpret it. Also, we’ll discuss how to read the Income Statement in the best possible way. Hopefully, this article will help you understand it better and avoid making common mistakes.
Helpful Links:
Homepage
About
Contact
Personal Development Partner